Avalanche Failure
A common failure mode caused by the voltage across the MOSFET drain-source exceeding its specified voltage and reaching a certain energy limit. The following test chart distinguishes whether it is an avalanche failure.
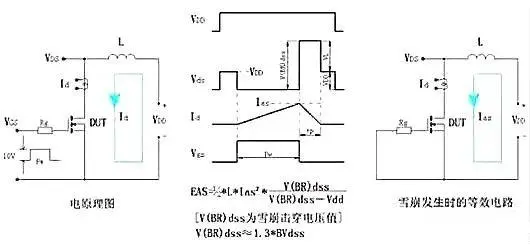
So, how can we effectively prevent the avalanche effect?
The main cause of the avalanche effect is voltage, so in terms of prevention, we will focus on voltage:
Reasonable derating, currently, derating in the industry is generally selected from 80% to 95%;
Reasonable transformer reflected voltage;
Reasonable RCD and TVS absorption circuit design;
Use thick and short layout structures for high current wiring to reduce wiring parasitic inductance;
Select a reasonable gate resistor Rg;
In high-power supplies, appropriately add RC shock absorption or Zener diodes for absorption.
SOA Failure (Current Failure)
Refers to the destruction mode caused by the abnormal large current and voltage superimposed on the MOSFET during operation, resulting in instantaneous local heating. Or it may be due to the failure to achieve thermal equilibrium between the chip and the heatsink and package in time, resulting in heat accumulation, and continuous heating causing the temperature to exceed the oxide layer limit, leading to thermal breakdown mode.
Preventive measures for SOA failure
Ensure that under worst-case conditions, all power limiting conditions of the MOSFET are within the SOA limiting line.
Make the OCP function precise and meticulous. When designing the OCP point, generally, it is mostly possible to take 1.1-1.5 times the current margin, and then adjust the RSENSE resistor according to the IC's protection voltage, such as starting with 0.7V.
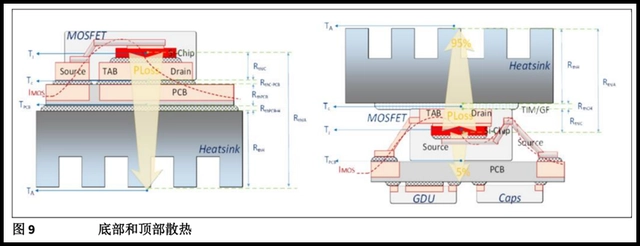
Reasonable thermal design margin, such as adding a heatsink.
MOSFET Heating Analysis
MOSFET heating is generally caused by exceeding the safe operating area.
The reasons for heating are generally divided into DC power and transient power:
DC power:
Conduction resistance RDS(on) loss, RDS(on) increases at high temperatures, causing an increase in power dissipation at a certain current;
Loss caused by leakage current IDSS (relatively small compared to other losses);
Transient power:
External single-trigger pulse;
Load short circuit;
Switching loss (turn-on, turn-off), which is related to temperature and operating frequency;
Loss of trr of built-in diode (short circuit loss of upper and lower bridge arms), which is related to temperature and operating frequency;
To generally solve the heating problem of MOSFETs, it is necessary to determine whether it is caused by the above reasons and conduct correct tests to find out the problem.
In the switch power supply test, a multimeter can be used to measure the pin voltage of other components in the control circuit, focusing on measuring the relevant voltage waveforms with an oscilloscope.
When judging whether the switch power supply is working normally, such as the working status of the power supply, whether the primary and secondary of the transformer and the output feedback are reasonable, whether the switching MOSFET is working normally, whether the PWM controller output is normal, including the pulse amplitude and duty cycle, etc.
Measures to solve the problem:
Change the value of the gate drive resistor, select the appropriate frequency, and create conditions for the MOSFET to conduct fully;
Select MOSFETs with lower internal resistance to reduce the voltage drop across the tube itself;
Reasonably select the heatsink.
In addition, other common failure effects of MOSFETs are:
Body Diode Failure
In topologies such as bridges and LLCs that require the use of body diodes for freewheeling, failures caused by damage to the body diode (PN junction).
Prevention:
Choose MOSFETs with shorter recovery times.
Optimize circuit design.
Electrostatic Discharge Failure
When the MOSFET is subjected to electrostatic discharge, device failure may occur.
Prevention:
Use electrostatic protection circuits to protect the MOSFET.
Gate Voltage Failure
Due to abnormal voltage spikes on the gate, causing the gate oxide layer to fail.
Prevention:
Choose the appropriate MOSFET model, or use overvoltage protection circuits to protect the MOSFET.
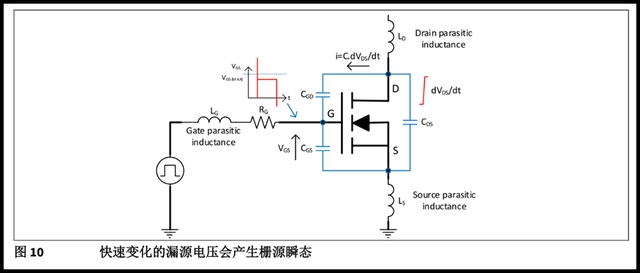
Resonance Failure
During parallel operation, failures caused by oscillations due to parasitic parameters of the gate and circuit.
Prevention:
When wiring the PCB, the wiring should be as short as possible, especially the MOSFET drive signal line;
Series resistors in the drive loop to increase damping;
Use compensation circuits to eliminate resonance effects.
* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您