In practical electronic applications, we often come across MOSFETs and IGBTs, both of which can be used as switching elements. So why do some circuits use MOSFETs while others use IGBTs? The answer lies in the different internal structures of MOSFETs and IGBTs, which determine their respective application areas.
Today, let's talk about the differences between MOSFETs and IGBTs, mainly from the following aspects:
Definitions
Working Principles
Performance Comparison
Application Analysis
Considerations for Selection
Definitions:
MOSFET:
The full name is Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor, also known as an Insulated-Gate Field-Effect Transistor (IGFET). It can be divided into four main types: N-channel depletion-mode and enhancement-mode MOSFETs, and P-channel depletion-mode and enhancement-mode MOSFETs.
Characteristics: High input impedance, fast switching speed, good thermal stability, voltage-controlled current, etc. It is generally used for amplifiers, electronic switches, and other purposes.
IGBT:
The full name is Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor, which is a composite semiconductor device composed of a bipolar transistor and a MOSFET.
Characteristics: High input impedance, low voltage-controlled power consumption, simple control circuit, high voltage resistance, and large current capacity. It is commonly used in applications such as AC motors, inverters, switch-mode power supplies, lighting circuits, and traction drives.
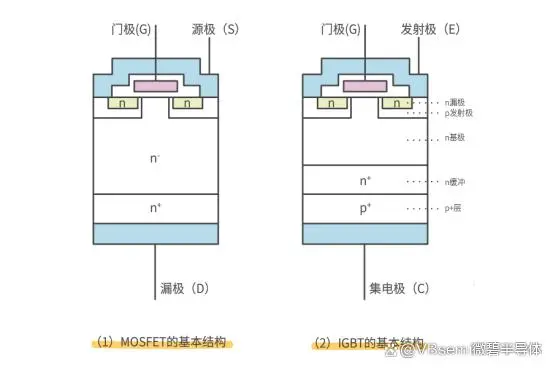
Working Principles:
MOSFET: Composed of source, drain, and gate terminals, it controls the current between the drain and source by changing the gate voltage.
When the gate voltage is positive, an N-type channel is formed, and current flows from the drain to the source; When the gate voltage is negative, the channel is cut off, and no current can pass through.
IGBT: Composed of emitter, collector, and gate terminals, it controls the current between the collector and emitter by controlling the gate voltage.
When the gate voltage is positive, electrons are injected from the P-type region into the N-type region, forming a conductive channel, and current flows from the collector to the emitter; When the gate voltage is negative, the channel is cut off, and no current can pass through.
Performance Comparison:
Power Handling Capacity:
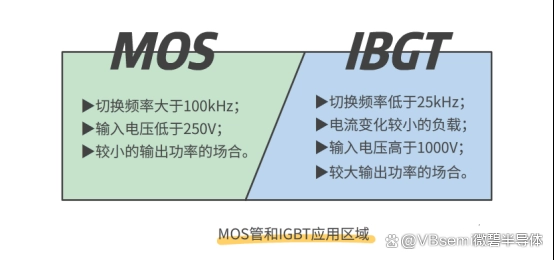
MOSFET: Compared with IGBTs, MOSFETs have an advantage in low and medium power applications. Due to the structure of MOSFETs, they can handle large currents, up to several KA, but they do not have the strong voltage resistance of IGBTs.
IGBT: It has higher efficiency in handling high voltage and large current, and has superior performance in high-power applications. It can handle high power, current, and voltage, but its frequency is not too high.
Switching Speed:
MOSFET: The switching speed of MOSFETs is very fast, which is a great advantage. The operating frequency of MOSFETs can reach several hundred KHz, MHz, or even tens of MHz.
IGBT: Currently, the hard switching speed of IGBTs can reach 100 KHz. Although the switching speed of IGBTs is not as fast as that of MOSFETs, they can still provide good performance.
Conduction and Switching Losses:
MOSFET: In applications with minimal Eon losses such as ZVS and ZCS, due to their fast switching speed, MOSFETs have shorter conduction times, allowing MOSFETs to operate at higher frequencies.
MOSFETs have much lower turn-off losses than IGBTs, mainly due to the tail current and dead time of IGBTs.
Temperature Characteristics and Voltage Drop:
Generally, the temperature coefficient of MOSFETs is lower than that of IGBTs, and MOSFETs have more stable performance in high-temperature environments.
Due to different design principles, the forward voltage drop of IGBTs is larger than that of MOSFETs. However, in many applications, the high voltage drop of IGBTs is offset by other advantages, such as high transient voltage withstand capability and lower conduction losses. Therefore, in high-voltage applications, IGBTs are more suitable.
Cost:
IGBTs are more expensive than MOSFETs due to their complex manufacturing process and high power handling capacity. Therefore, in some cost-sensitive applications and low-power, high-frequency application scenarios, MOSFETs are the preferred choice due to their lower cost and flexibility.
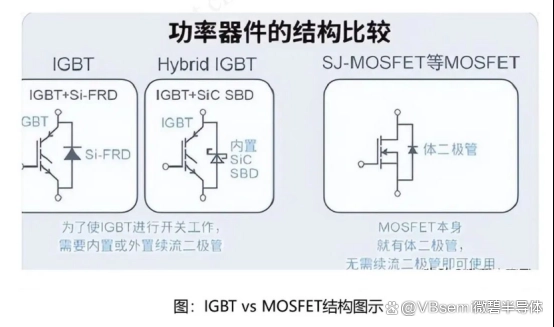
Application Advantages:
MOSFET: Advantageous in high-frequency switching applications.
The advantages of MOSFETs make them very suitable for high-frequency applications with high switching speed requirements. In the field of switch-mode power supplies, the parasitic parameters of MOSFETs are crucial, as they determine switching time, conduction resistance, ringing (overshoot during switching), and back-gate breakdown performance.
IGBT: Advantageous in high-voltage and large current applications.
IGBTs have a great advantage in handling and conducting extremely high voltages and large currents. Due to its very high gate insulation characteristics and extremely low forward voltage drop during current conduction, IGBTs can operate without interference even when surge voltages occur.
However, compared with MOSFETs, IGBTs have slower switching speeds and longer turn-off times, making them unsuitable for high-frequency applications.
Considerations for Choosing MOSFETs and IGBTs:
Selection of MOSFETs in Different Fields:
When selecting MOSFETs as power switches,
Pay attention to their extremely low conduction resistance, low input capacitance, and high gate breakdown voltage, which can even handle any peak voltage generated by inductance;
The lower the parasitic inductance between the drain and source, the better, because low parasitic inductance can reduce the peak voltage during switching to a minimum.
Selection of MOSFETs for Gate Drivers or Inverter Applications:
Generally, choose MOSFETs with low input capacitance (beneficial for fast switching) and higher driving capability to ensure better driving capability.
Considerations for IGBT Parameter Selection in Applications:
Rated Voltage: Under switching conditions, the rated voltage of IGBTs is usually higher than twice the DC bus voltage;
Rated Current: Due to the easy current overload during load electrical start-up or acceleration, IGBTs are required to withstand 1.5 times the overload current within 1 minute;
Switching Speed: This is self-evident, good switching speed helps the switch to work better;
Gate Voltage: The working state of IGBTs is closely related to the forward gate voltage. Generally, the higher the voltage, the lower the switching loss and the smaller the forward voltage drop.
In summary, although MOSFETs and IGBTs have similar external shapes and characteristic parameters, their applications and effects are quite different.
(Original creation is not easy, if you've made it this far, could you please like or follow? Thank you for your support!)
However, generally speaking, there is no fundamental difference between MOSFETs and IGBTs. We often hear the question "Is MOSFET better or IGBT better?" In fact, there is no such thing as a choice. For example, as mentioned at the beginning, sometimes circuits use MOSFETs, and sometimes they use IGBTs, which is determined by their respective advantages in various application fields, and cannot be simply distinguished or judged by good or bad.
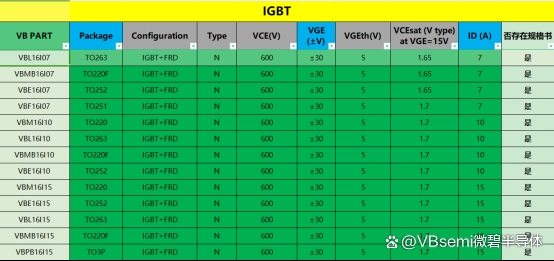
Similarly, choosing the appropriate and performance-optimized products is also very important. Here, I recommend VBsemi's MOSFETs and IGBTs, which are suitable for a variety of application fields and have excellent device performance.

* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您