Previously, VBsemi has released a post titled "What are the Advantages of NMOS over PMOS in DC-DC Converters?" which briefly introduced some differences and advantages of NMOS and PMOS in applications. Today, we will discuss in detail why NMOS is more popular than PMOS in practical applications. If you find this article helpful, please like and follow for more!
This article will focus on several aspects such as channel conductivity, electron mobility, and device speed.
Firstly, let's consider performance:
For a PMOS transistor with the same driving capability as an NMOS transistor, its device area may be 2 to 3 times that of the NMOS transistor. However, the device area affects on-resistance and input-output capacitance, which can easily lead to circuit delays.
Similarly, under the same size conditions, the channel on-resistance of a PMOS transistor is slightly larger than that of an NMOS, resulting in correspondingly larger switch-on losses for the PMOS transistor.
Now let's delve deeper into the channel:
The channel of an NMOS is made of n-type semiconductor, while the channel of a PMOS is made of p-type semiconductor. Due to the higher electron concentration in n-type semiconductor compared to p-type semiconductor, the electron mobility of NMOS is higher. This means that under the same electric field, electrons in NMOS move faster than electrons in PMOS.
It's worth mentioning that the difference in mobility leads to differences in speed and channel on-resistance, limiting the application range of PMOS.
In terms of manufacturing process, there is not much difference between PMOS and NMOS transistors. With the continuous advancement of technology, this difference has become smaller and smaller.
So, why do electrons in NMOS have higher mobility and move faster than those in PMOS?
Let's briefly understand electron/hole mobility:
Electron mobility refers to the speed at which electrons move under the influence of an electric field.
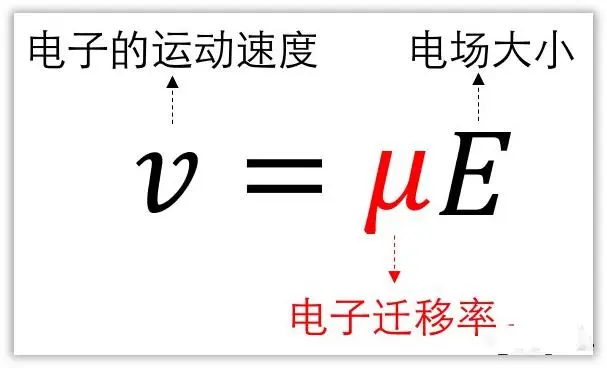
For two semiconductor materials with the same electron concentration, generally, the semiconductor material with higher mobility will have faster electron movement speed, leading to a larger number of electrons passing through in a unit of time, i.e., a larger current.
Therefore, the higher the electron mobility of a semiconductor material, the lower its resistivity, and the smaller its loss when the same current passes through.
Hole mobility is similar to electron mobility, where higher hole mobility leads to smaller losses.
However, under normal circumstances (as mentioned above), electron mobility is higher than hole mobility.
This is because a hole is the absence of an electron, and the movement of a hole is essentially the movement of an electron from one hole to another.
Now, let's go back to the difference in channel conductivity between NMOS and PMOS.
MOS transistors have only one type of charge carrier, either electrons or holes. When a bias voltage is applied, an inversion layer is formed as the conductive channel, which is the path for charge carrier migration.
When an NMOS is conducting, it forms an N-type conductive channel, meaning it conducts using electrons. On the other hand, when a PMOS is conducting, it forms a P-type conductive channel, conducting using holes. Here's a simple note:
NMOS has an N-type channel, and the charge carrier is electrons.
PMOS has a P-type channel, and the charge carrier is holes.
Generally, the electron mobility is five to ten times that of hole mobility. Depending on the material, structure, and characteristics, this ratio can be even higher.
Because electrons have higher mobility than holes, under the same volume and doping conditions, the losses of NMOS are much smaller than those of PMOS.
Apart from power consumption, electron/hole mobility also affects the speed of the device.
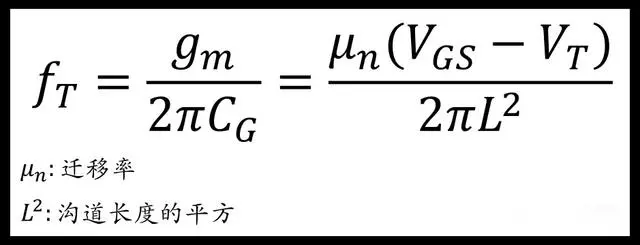
The cutoff frequency of an NMOS (the frequency when input/output=1)
From the result, the cutoff frequency is proportional to the electron mobility.
Therefore, the higher the electron mobility, the higher the working frequency of the NMOS.
When the Vgs voltage of an NMOS changes at a high frequency, the thickness of the conductive channel also changes accordingly.
This change in the conductive channel is caused by the movement of electrons. The faster the movement of electrons (i.e., the higher the electron mobility), the faster the conductive channel responds to the change in Vgs, which involves the working principle of the NMOS.
This indicates that the higher the electron mobility, the higher the device's operating frequency.
The same applies to PMOS.
In addition to the above aspects, there are other factors contributing to the popularity of NMOS, such as price. Generally, PMOS on the market is more expensive than NMOS. This is due to various factors in the market economy. After comprehensive consideration, NMOS is chosen more often when selecting MOS transistors.
In summary, here are the reasons why NMOS is more popular in practical applications:
The channel on-resistance of NMOS is much smaller than that of PMOS, resulting in lower switch-on losses.
NMOS has an N-type channel, and the charge carrier is electrons; PMOS has a P-type channel, and the charge carrier is holes. Electron mobility is higher than hole mobility, giving NMOS advantages in terms of losses and switching speed.
NMOS has a larger current-carrying capacity than PMOS.
Other factors such as price also play a role.
Disclaimer: Some of the information and images in this article are from the internet.
* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您