The MOSFET bridge rectifier is a bridge rectifier circuit implemented using MOSFET devices, used to convert AC to DC. It consists of four MOSFETs and enables efficient energy conversion.
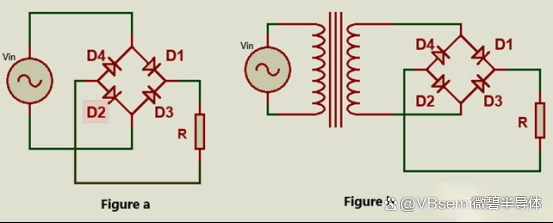
When the input AC is in the positive half-cycle:
MOSFET 1 and MOSFET 4 conduct, while MOSFET 2 and MOSFET 3 are off, allowing current to flow from the input to the output.
When the input AC is in the negative half-cycle:
MOSFET 2 and MOSFET 3 conduct, while MOSFET 1 and MOSFET 4 are off, maintaining current flow from input to output.
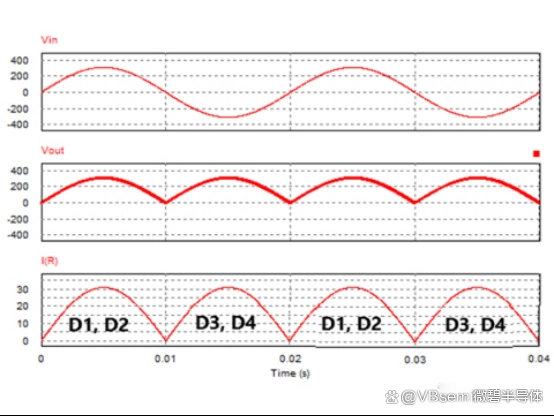
This switching allows the MOSFET bridge rectifier to convert AC to DC by enabling conduction in both positive and negative half-cycles, achieving rectification.
Lower conduction resistance of MOSFETs leads to lower power losses and higher efficiency.
Strong controllability allows for more precise voltage and current control.
Longer lifespan and greater stability in high-temperature environments.
Electromagnetic interference during switching.
Output voltage ripple affects downstream circuits.
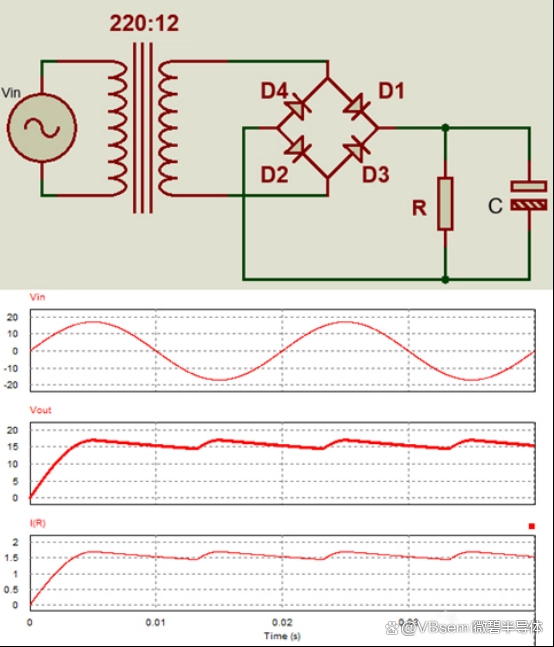
MOSFET bridge rectifiers are commonly used in PC power supplies to convert AC to DC for internal components. They improve efficiency and controllability while reducing the size of the power supply.
By converting input AC to DC with low output voltage ripple and high efficiency, MOSFET bridge rectifiers play a crucial role in PC power supplies. They should be used with filter capacitors to reduce output voltage ripple.
Disclaimer: Some images and content in this article are sourced from the internet. Please verify carefully.
Disclaimer: Some images and content in this article are sourced from the internet. Please verify carefully.

* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您