When selecting and using MOSFETs, we often consult the product datasheet. However, facing a plethora of parameters can sometimes be overwhelming. Today, we will interpret some of the more basic and commonly used parameters in datasheets to help you more easily choose the right MOSFET products.
Let's take a look at the following chart:
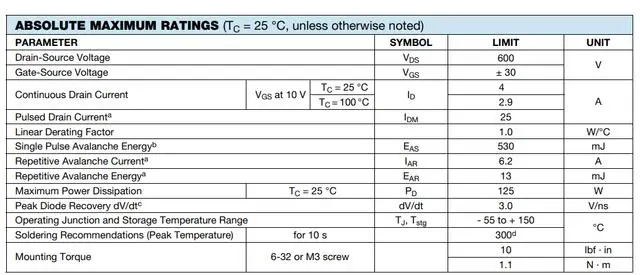
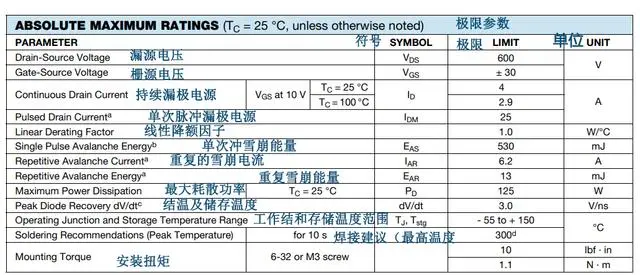
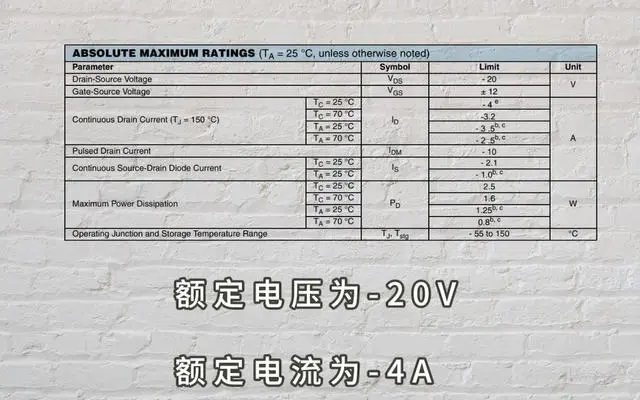
VDS: Drain-Source Voltage, the voltage between the drain and source when the MOSFET is operating (maximum rating).
VGS: Gate-Source Voltage, the voltage between the gate and source when the MOSFET is operating (maximum rating).
ID: Drain Current (continuous current rating), the current flowing from the drain when the MOSFET is operating. If the current exceeds this value, there is a risk of breakdown.
IDM: Maximum Pulsed Drain Current (single-pulse current rating between source and drain), the maximum instantaneous drain current that the MOSFET can withstand. Similarly, exceeding this value can cause breakdown.
EAS: Single-Pulse Avalanche Energy, the energy of a single pulse that the MOSFET can withstand safely, absorbing the energy of reverse avalanche breakdown.
PD: Maximum Power Dissipation, the maximum power that the MOSFET can withstand.
DV/dt: Drain-Source Voltage Rate of Change (the higher the better), the rate of change of drain-source voltage per unit time.
TJ, Tstg: The temperature range in which the MOSFET can operate normally and can be safely stored. Operating the device within the appropriate temperature range will help extend its service life.
These parameters have a significant impact on the operation and performance of MOSFETs.
Among them, VDS and VGS are the basic operating voltages of MOSFETs, ID and IDM determine the output current capability of MOSFETs, EAS and PD define the safe operating range of MOSFETs, and DV/dt is the switching speed of MOSFETs. The operating junction temperature range and storage temperature range are environmental restrictions for MOSFETs.
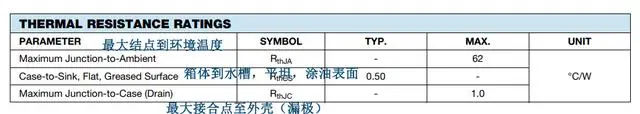
RthJA and RthJC indicate the thermal resistance values of MOSFET devices, one is the maximum thermal impedance between the channel and the environment, and the other is the maximum thermal impedance between the channel and the package. Generally, the smaller the thermal resistance, the better the heat dissipation performance.
It can help us calculate the maximum operating temperature and power of the MOSFET device. If the operating temperature of the MOSFET device exceeds its maximum operating temperature, it may be damaged or fail.
These are generally the most common parameters. There are more parameters and curve charts that we will explain in future posts.
In the face of so many parameters, VBsemi has recently integrated some product videos to help you quickly find the MOSFET models you are looking for, and will continue to promote them in the future. (As shown in the picture below)
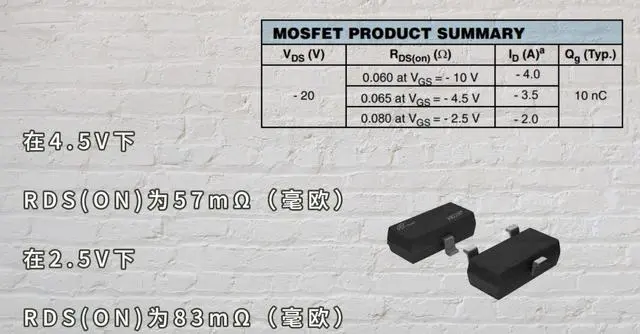
Product packaging, channel type, maximum current, maximum voltage, limiting voltage and threshold voltage, RDS(on) parameters (under different conditions), other parameters, and their wide range of application fields.
(Video content)
When facing MOSFET products you want to understand, you can directly search for the product model, or if you are not sure which MOSFET products are suitable for you, you can click to view on various platforms to see which products match your application situation. You can also choose to search the official website for more product parameter details!
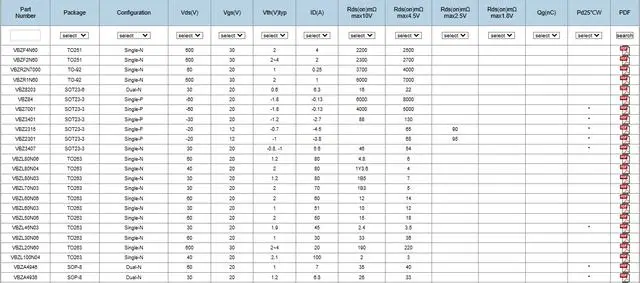
(VBsemi Model Catalog)
This article is compiled from online sources. If you have any questions, please feel free to discuss them in the comments section! VBsemi insists on producing popular science articles every day, and your support is the driving force behind our creation. Like and follow us if you enjoy our content!
* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您