A commenter in the previous post asked for an article on common mainstream circuit designs for MOSFETs.
Better late than never! Today, let's explore several common MOSFET driver circuit designs (but not limited to these) and how to choose the right driver circuit to drive MOSFETs.
MOSFETs, with advantages such as low on-resistance and fast switching speed, are widely used in switch-mode power supplies. Therefore, the design of the driver circuit for a MOSFET is critical.
Power IC Driver Circuit
One common MOSFET driver circuit design. It uses an integrated power IC as the driver chip to control the switching state of the MOSFET by providing appropriate power voltage and current. This design is simple, reliable, and can provide stable drive signals.
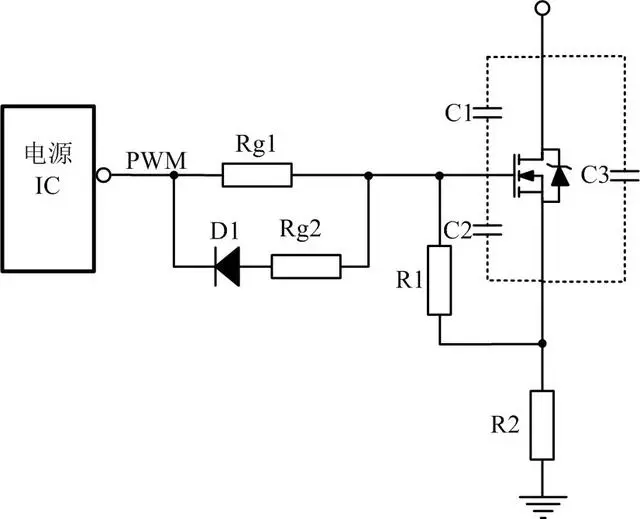
(Part of the pictures are from the internet)
Push-Pull Driver Circuit
Another common MOSFET driver circuit design. It consists of two drivers connected in reverse parallel. One driver is used to drive the gate of the MOSFET to a high level, and the other driver is used to drive the gate of the MOSFET to a low level. By alternately controlling the two drivers, the push-pull driver circuit can achieve forward and reverse driving of the MOSFET, thereby amplifying and outputting the signal.
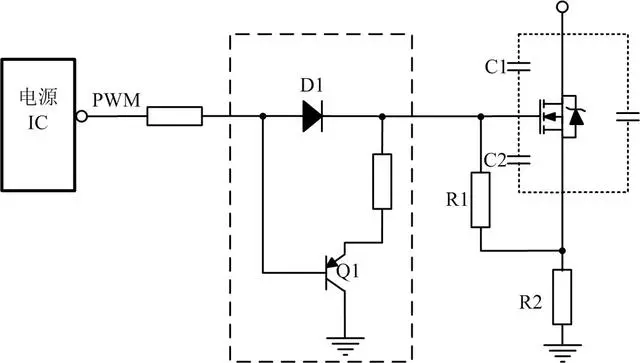
Half-Bridge Driver Circuit
Especially suitable for driving two series-connected MOSFETs. It consists of two drivers, one driver for controlling the upper MOSFET and the other driver for controlling the lower MOSFET. By alternately controlling the two drivers, the half-bridge driver circuit can achieve forward and reverse driving of the two MOSFETs, thereby amplifying and outputting the signal.
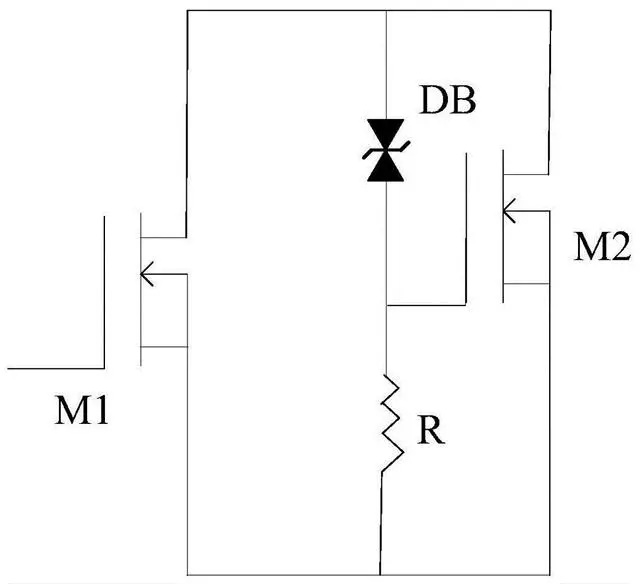
Fast Turn-off Driver Circuit
Used to improve the turn-off speed of the MOSFET. It applies a high-voltage pulse to the MOSFET during the turn-off process, quickly turning off the MOSFET, thereby reducing power loss and heat generation during switching.
How to choose the right driver circuit design to drive MOSFETs?
The drive current should be sufficient: Sufficient drive current ensures that the gate-source voltage of the MOSFET rises rapidly to the required level, ensuring fast turn-on of the MOSFET and improving the efficiency of the circuit.
The drive voltage should be moderate: Excessive drive voltage may cause the gate-source voltage of the MOSFET to overshoot, affecting its lifespan.
Low output impedance: Low output impedance ensures stable output voltage of the driver circuit, thereby improving the switching performance of the MOSFET.
Some information in this post is from the internet. Actual application requires analysis based on specific conditions.
If there is any other knowledge you would like to discuss and explore, please leave a comment in the comment section! If you're interested, please follow us! See you next time!
* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您