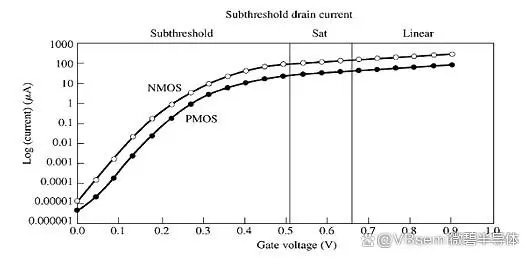
The principle of sub-threshold conduction in MOS transistors refers to the scenario where the gate voltage of the MOS transistor is lower than the threshold voltage, yet there is still a small current passing through. This is because under sub-threshold conditions, a reverse-biased diode is formed between the gate and the source, allowing a small leakage current to pass through.
In the sub-threshold region, the conduction mechanism of the MOS transistor is primarily determined by the sub-threshold current on the drain side.
When the gate voltage is lower than the threshold voltage, a reverse-biased diode forms between the gate and the drain, causing the sub-threshold current to flow on the drain side.
The sub-threshold conduction phenomenon is due to the presence of sub-threshold current. In the sub-threshold region, the sub-threshold current of the MOS transistor increases with the increase of gate voltage. However, as the gate voltage further increases, the MOS transistor gradually enters the saturation region, at which point the sub-threshold current on the drain side begins to decrease.
How does the sub-threshold conduction phenomenon affect circuit performance?
The occurrence of sub-threshold conduction is usually due to factors such as temperature variations, process deviations, or device aging.
Impact 1: Increased power consumption
Sub-threshold conduction can cause MOS transistors to still have a certain leakage current in the off state, thereby increasing the static power consumption of the circuit. Especially for circuits with a large number of MOS transistors in Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI), this additional power consumption may significantly increase the overall system power consumption.
Impact 2: Decreased signal integrity
Sub-threshold conduction also has a certain impact on signal integrity.
In some highly sensitive analog circuits, even a small leakage current can cause signal offset or distortion. Additionally, sub-threshold conduction may also lead to a decrease in signal magnitude or instability.
How to control sub-threshold conduction by changing the gate voltage?
One method to control sub-threshold conduction by changing the gate voltage is to use Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFETs).
In MOSFETs, sub-threshold conduction is mainly achieved by varying the gate voltage. When the gate voltage is below the threshold voltage, the channel of the MOSFET narrows but still conducts a certain amount of current. By increasing the gate voltage, the channel width can be increased, thereby reducing sub-threshold conduction.
The following methods can be used:
Modulation technique: Modulate sub-threshold conduction by varying the gate voltage. When the gate voltage is below the sub-threshold voltage, the device is in the off state; when the gate voltage is higher than the sub-threshold voltage, the device starts to conduct.
Increase gate current: Increasing the gate current enhances sub-threshold conduction. The higher the gate current, the higher the probability of sub-threshold conduction.
Apply feedback voltage near the sub-threshold voltage: Applying feedback voltage near the sub-threshold voltage can change the difference between the gate voltage and the source voltage, thereby affecting sub-threshold conduction.
In addition to changing the gate voltage, are there other methods to control sub-threshold conduction?
Control drain voltage: Control sub-threshold conduction by changing the drain voltage. When the drain voltage is below the sub-threshold voltage, the transistor remains in the off state; when the drain voltage is higher than the sub-threshold voltage, the transistor starts to conduct.
Control base current: For Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs), sub-threshold conduction can be controlled by controlling the base current. When the base current is lower than the sub-threshold current, the BJT is in the cutoff region; when the base current is higher than the sub-threshold current, the BJT starts to conduct.
Control source voltage: For Field-Effect Transistors (FETs), sub-threshold conduction can be controlled by changing the source voltage. When the source voltage is below the sub-threshold voltage, the FET remains in the off state; when the source voltage is higher than the sub-threshold voltage, the FET starts to conduct.
The above methods all involve changing relevant parameters to control the conduction state of the transistor, thereby achieving control of sub-threshold conduction.
(Sources from the internet, discretion is advised in practical applications)
Microgreen VBsemi
Product Packaging
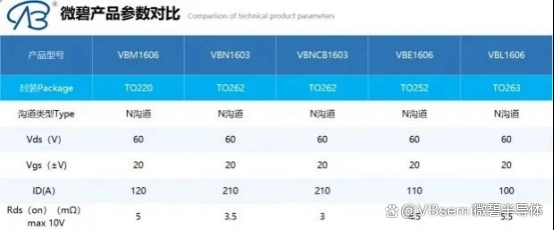
Microgreen products include SOT23, DFN, SOT-89, SOP-8, TO-92, TO-251, TO-252, TO-220, TO-220F, TO-263, TO-247, SOT-223, TO3P, TO262, SOT669, TSSOP8, SC70, DIP8, SC75, SOT725 and other series of packaging products to meet various needs of users.
Application Areas
Microgreen products are widely used in the automotive field: electronic control, battery management, onboard inverters, onboard electronic products, charging piles, etc.; communication field: various power supplies, switches, etc.; industrial field: inverters, frequency converters, power tools, etc.; home appliance field: fans, washing machines, sweeping robots, refrigerators, air conditioners, etc.; consumer electronics field: lighting lamps, medical equipment, wireless charging, mobile power supplies, etc., and the product quality has always maintained at the top level in the industry.
If the above content is helpful to you, please like + follow! Thank you!
* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您