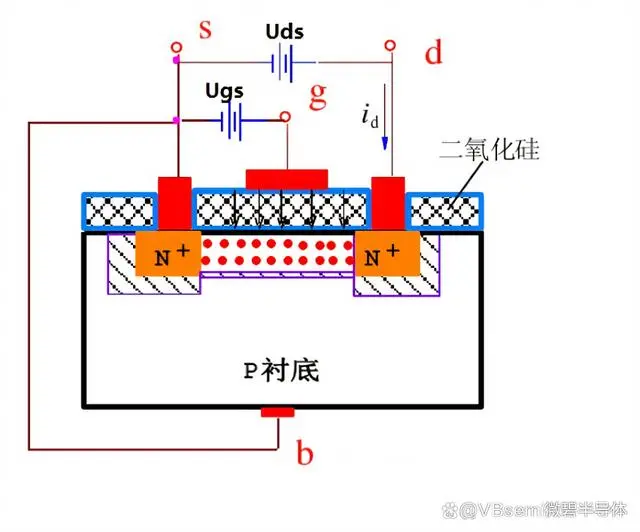
We know that leakage current can lead to power consumption, especially at lower threshold voltages. Below, we will discuss the six main reasons for leakage current in MOSFETs.
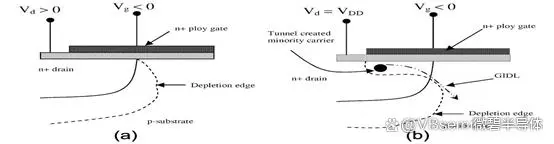
Gate current
The leakage current in MOSFETs is caused by imperfections in the material or manufacturing process. For example, the insulation layer inside the MOSFET may have defects, leading to incomplete blocking of the leakage current. Additionally, impurities or defects inside the MOSFET may also cause leakage current.
Solution: Improve the quality control of the manufacturing process, reduce the presence of impurities and defects, and increase the quality of the insulation layer.
Thermal carriers
Thermal carriers refer to carriers that mainly result from energy loss of carriers in the device. When the MOSFET is operating, the scattering and collision of carriers in the channel generate heat. This heat energy increases the energy of the carriers, causing some carriers to cross the channel barrier, increasing the leakage current.
Solution: Optimize the device structure and materials to reduce the generation of thermal leakage. The leakage current can be reduced by changing the channel length, increasing the thickness of the insulation layer, etc. Measures such as reducing the operating temperature and reducing the power supply voltage can also reduce thermal leakage.
PN junction reverse saturation current
The drain/source and substrate junctions of the MOSFET are reverse biased. Due to the drift/diffusion of minority carriers in the reverse biased region and the formation of electron-hole pairs due to the avalanche effect, a reverse current is generated. This reverse current increases power consumption and loss.
Solution:
Add a reverse current suppression circuit in the reverse circuit of the MOSFET to effectively reduce the magnitude of the reverse leakage current. The reverse leakage current increases exponentially with the junction temperature. Controlling the junction temperature of the MOSFET can reduce the magnitude of the reverse leakage current.
Substrate leakage
Substrate leakage: Substrate leakage is the leakage current caused by the electric field between the substrate and other electrodes. Substrate leakage is related to the electric field strength between the substrate and the source electrode, electron mobility, and device size.
Solution: Strengthen the insulation between the substrate and other electrodes to reduce the impact of the electric field.
Drain leakage
Drain-source current is the leakage current caused by the interaction of the depletion regions between the drain and source, reducing the source barrier and leading to leakage current.
Solution: Optimize device structure and design to reduce the impact of the depletion region.
Subthreshold leakage
Subthreshold leakage is the leakage current caused by injecting charge carriers into the channel surface from the source. In the subthreshold region, there is a small accumulation of charges in the channel, resulting in a small leakage current.
(Tip: In weak inversion, the concentration of minority carriers is very small but not zero.)
Solution: Reduce subthreshold leakage by optimizing device structure and process parameters.
(Some information from the internet)
These are the six main reasons for leakage current in MOSFETs. Of course, there are other factors, large and small, that can affect the leakage current of MOSFETs, and we can explore them together in the future!
That's all for today's VBsemi Science Popularization. Creating is not easy, so if you like it, can you please follow us?
* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您