We often mention NMOS and PMOS, and in the past, VBsemi has talked about their applications in various fields. However, there has been little in-depth discussion about the basic characteristics of these two. Today, we will briefly explain the differences between them, focusing on current and conduction conditions.
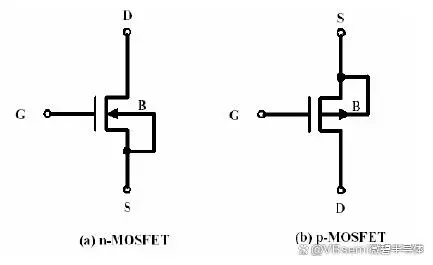
NMOS current flow direction and conduction conditions:
NMOS (N-channel MOSFET)
Current flow direction:
The current flow direction of NMOS is from the source (S) to the drain (D). When a forward bias voltage is applied between the gate (G) and the source, the current flows from the source to the drain, i.e., S-D.
Current can flow from D to S (nMOS) or from S to D (pMOS). It mainly depends on the potential between the source and the drain. If the drain potential is higher than the source potential, the current flows from D to S. If the source potential is higher than the drain potential, the current flows from S to D.
Conduction conditions:
The conduction condition of NMOS is when the voltage between the gate and the source (Vgs) is greater than or equal to the threshold voltage (Vth). The threshold voltage is a specific voltage that determines whether the MOSFET conducts. Once Vgs is greater than or equal to Vth, NMOS conducts. At this time, the voltage between the gate and the drain (Vgd) can be positive or zero.
PMOS current flow direction and conduction conditions:
The current flow direction and conduction conditions of PMOS (P-channel MOSFET) are as follows.
Current flow direction:
The current flow direction of PMOS is from the drain (D) to the source (S). When a reverse bias voltage is applied between the gate (G) and the source, the current flows from the drain to the source, i.e., D-S.
Conduction conditions:
The conduction condition of PMOS is when the voltage between the gate and the source (Vgs) is less than or equal to the threshold voltage (Vth). The threshold voltage is a specific voltage that determines whether the MOSFET conducts. Once Vgs is less than or equal to Vth, PMOS conducts. At this time, the voltage between the gate and the drain (Vgd) can be negative or zero.
S is the source, and D is the drain.
For NMOS, the current carriers are electrons, and the current flows from the drain to the source. For PMOS, the current carriers are holes, and the current also flows from the drain to the source, unlike NMOS where the current flows from the source to the drain.

* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您