This article explains the phenomenon of floating gate, its impact, and solutions from three aspects.
About the Concept of Floating Gate
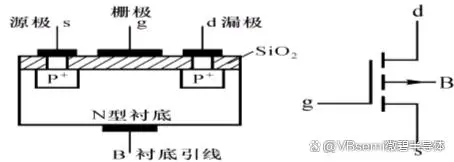
Floating gate refers to the condition where the gate of a MOSFET is not connected to any electrode and is in a suspended state. In this state, the gate voltage is zero, and the conduction characteristics of the MOSFET change (when Vg (gate voltage) inputs a high level, the N-channel conducts, causing the gate of the P-channel to be low, thus allowing the P-channel's DS (drain-source) to conduct. Conversely, when Vg is in a high impedance state, Vout (output voltage) input is indefinite, and it is found that the gate voltage of the P-channel changes indefinitely).
However, not all MOSFET gates must not float, as it depends on specific application scenarios and requirements.
So, what impact does a floating gate have on a MOSFET?
Imagine if the gate is floating, the electric field between the gate and the source-drain would disappear, rendering the MOSFET unable to function properly. More seriously, floating gate may cause the gate capacitance to fail, thereby affecting the stability of the entire circuit. Therefore, to ensure the normal operation of the MOSFET, we must ensure that the gate does not float.
Effects of the Floating Gate Phenomenon on MOSFETs
Affects the switching speed of MOSFETs: Increases the input capacitance of MOSFETs, reducing their switching speed.
Increases power consumption: Interference with the current between the drain and source of the MOSFET increases device power consumption.
Affects signal transmission quality: Floating gate may lead to signal transmission interference, reducing signal quality.
Trigger misoperation: May cause MOSFETs to mis-trigger when they should not be conducting, affecting circuit stability.
Solutions to the Floating Gate Phenomenon of MOSFETs:
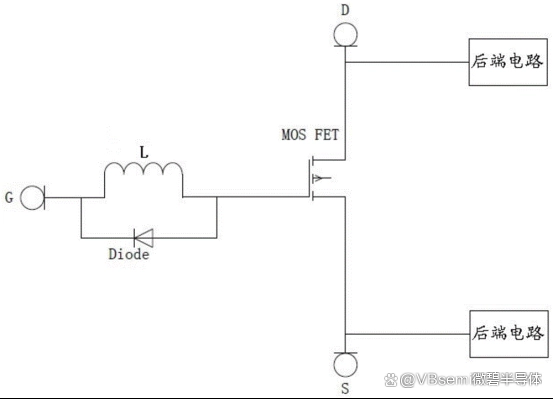
Increase protection resistance: To prevent electrostatic interference from affecting the gate of the MOSFET, a protection resistor can be connected in series between the gate of the MOSFET and the power supply. In this way, when electrostatic interference occurs, the protection resistor can guide most of the interference current to the ground, ensuring the stability of the MOSFET gate voltage.
Reduce the impact of parasitic capacitance: To reduce the impact of parasitic capacitance on the MOSFET gate voltage, the following methods can be used:
a. Select MOSFETs with lower parasitic capacitance; b. Reduce the size of the MOSFET; c. Connect a capacitor between the source and ground of the MOSFET to reduce the impact of parasitic capacitance.
Optimize grounding treatment: In circuit design, the stability of the grounding system should be ensured by using a single-point grounding method and ensuring that the grounding resistance is small enough. Additionally, shielding technology can be used to isolate the MOSFET from interference sources, reducing the impact of electromagnetic interference on the gate voltage.

* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您