The manufacturing process of MOSFETs is similar to that of other integrated circuits. It is based on wafer manufacturing, which starts with what people commonly call light.
Do you know how this invisible light is used to produce a delicate chip? And how is it used to produce it through a photolithography machine?
This time, let's explain it. In the important pre-process of chip manufacturing - photolithography technology.
First, we need to know that the three core processes of semiconductor manufacturing are photolithography, plasma etching, and vapor deposition. Among them, the main function of photolithography is to replicate the circuit pattern printed on the mask plate onto the substrate wafer, preparing for the next etching or ion implantation process.
Photolithography technology, as the name implies, is a carving technology that uses light as the medium. The most important reason why light plays a crucial role is because of its speed. For chip manufacturers, extremely high speed is required to meet the requirements and capacity of the corresponding technology. The important carrier used to control light and then carve out chips is photomasks, photolithography machines, and photoresists.

What is a photomask?
A photomask is an important device used in the manufacturing process of LSI and other integrated circuits. Extremely fine circuit patterns are processed on the light-shielding film on the surface of a transparent glass plate, becoming the original version for reproducing circuits on silicon wafers. The pattern on the photomask is reduced and projected onto the silicon wafer to form a fine pattern.
The photolithography machine, also known as a mask aligner, can be easily understood to be related to the photomask through its name.
Yes, the working principle of a photolithography machine is to use a series of light source energy and shape control means to transmit the light beam through the mask with the line pattern, compensate for various optical errors through the lens, proportionally reduce the line pattern, and then project it onto the silicon wafer. The circuit pattern etched on the silicon wafer is then obtained using a chemical method called development.

About photoresists
Photoresists are sensitive mixtures of photosensitive resin, sensitizer, and solvent. They are used as corrosion-resistant film materials in the photolithography process by changing their solubility after exposure or radiation with ultraviolet light, electron beams, ion beams, X-rays, etc.
In simple terms, a photoresist is a material that converts light and shadow into actual circuits. Negative resists produce insoluble substances that become insoluble in certain solvents after exposure to light; conversely, positive resists are soluble in certain solvents, become soft after exposure to light, and then become soluble substances.

So how do we use photolithography to manufacture chips? The figure below shows the steps of photolithography for everyone:
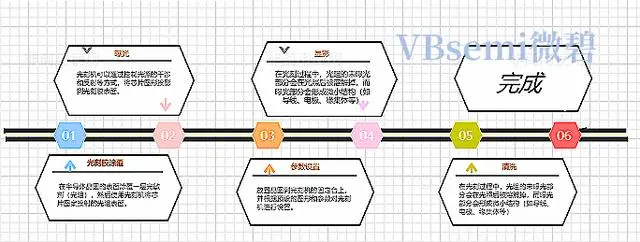
After completing the above steps, the next phase of steps, namely vapor phase etching and vapor phase deposition, can be carried out. Etching and deposition are important processes in the manufacture of chips, and these two areas will be discussed in detail later.
Therefore, through the above steps, we can understand that in a narrow sense, what photolithography carves is not the silicon wafer, but the layer of photoresist on the silicon wafer. By etching the photoresist, and then proceeding to the next etching and deposition steps, the silicon wafer can be processed with etching and post-processes.
Before each etching, deposition, and ion implantation step, a photolithography step is required. Therefore, photolithography is the foundation of all processes in chip manufacturing, occupying most of the time and cost of the entire process.
In conclusion, manufacturing chips with a photolithography machine is a highly precise process. It requires strict technical operations and the support of professional equipment. Photolithography technology is a key process for promoting the development of integrated circuits and related industries. The iterative upgrading of photolithography technology has greatly improved the computing speed and storage capacity of chips, and it has been widely used in important technical fields such as industrial control, aerospace, national defense technology, new energy, and smart cities.
We must believe that as long as we successfully master the methods and technologies, manufacturing high-quality chips will no longer be an impossible task.


* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您