
With the rapid development of modern society and the acceleration of life pace, more and more people are paying attention to their health, especially cardiovascular diseases. According to statistics from the World Health Organization, cardiovascular disease is one of the leading causes of death globally. In recent years, there has been a noticeable trend of cardiovascular diseases such as sudden cardiac death and myocardial infarction occurring at a younger age, which has raised high concerns.
To address this issue, major consumer electronics giants have introduced electronic devices with heart rate monitoring functions, such as smart bracelets and smartwatches. However, these consumer-grade electronic devices suffer from issues such as errors caused by wearing methods, baseline drift, motion artifacts, and inaccurate QRS recognition, which affect the accuracy and reliability of the data.
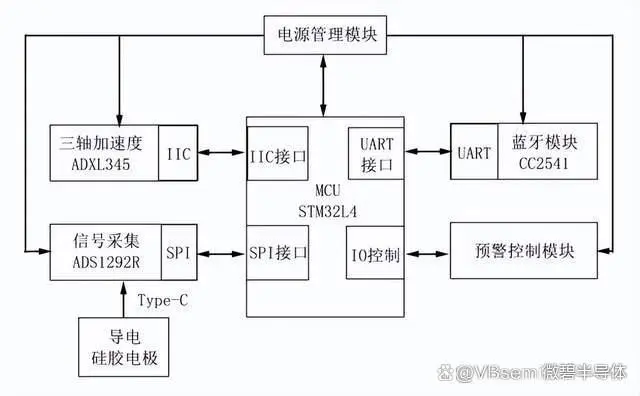
To solve these problems, Chen Ya Jun designed a wearable portable ECG monitoring device based on low-power components and an improved adaptive filtering algorithm. The device uses MOSFET switch circuitry to switch between charging and power supply states, and employs hardware modules such as a three-axis accelerometer and a signal acquisition module to collect three-axis acceleration signals from the human body, sense the intensity of relative body movement, and optimize the filtering effect of the algorithm to output "clean" ECG signals. The prototype is compact with dimensions of only 39mm x 20mm, has long battery life, low power consumption, and fast charging advantages.
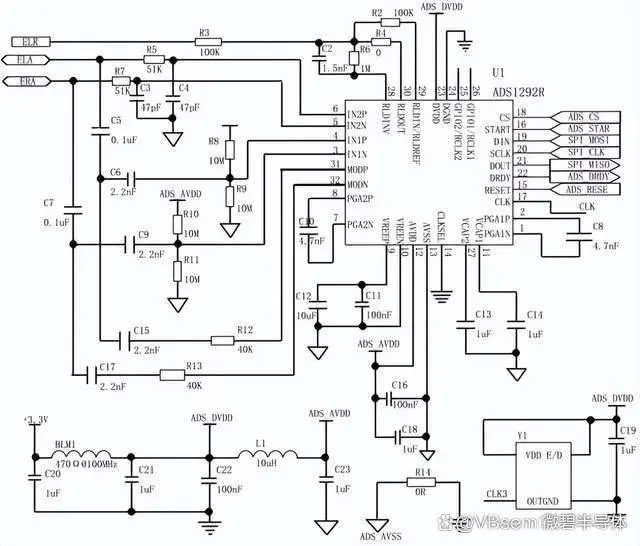
In the hardware design of the device, the signal acquisition module uses the ADS1292R analog-to-digital converter chip.
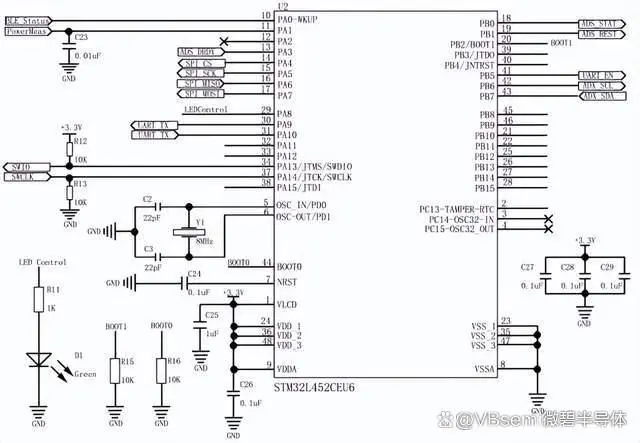
The main control chip uses the STM32L452CEU6.
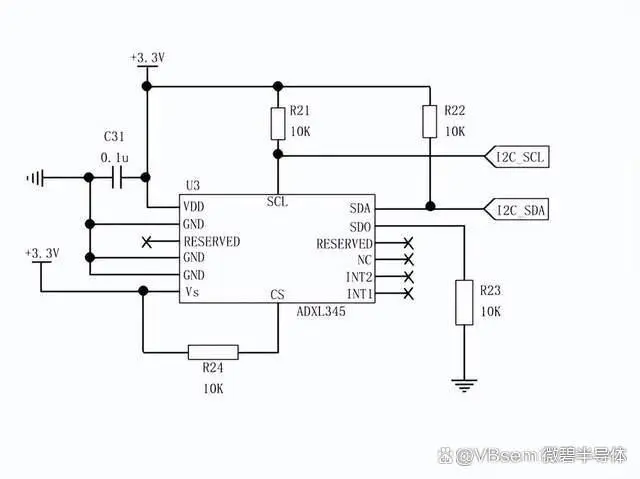
The three-axis acceleration module uses the ADXL345BCCZ accelerometer chip.
The wireless transmission module uses the B-0004 low-power Bluetooth 4.0 module.
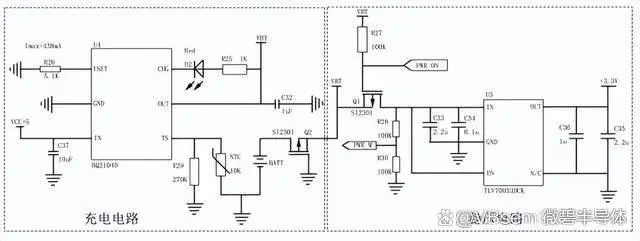
The charging module uses the BQ21040 power management chip, and the voltage regulator chip uses the TLV70033DCK regulator.
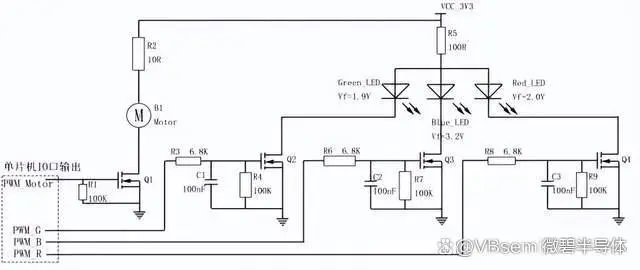
In the warning control circuit for light sources, a tri-color RGB LED and a miniature vibration motor are used to achieve illumination and vibration. NMOS and PMOS transistors are selected as the switching devices in the switch circuit.
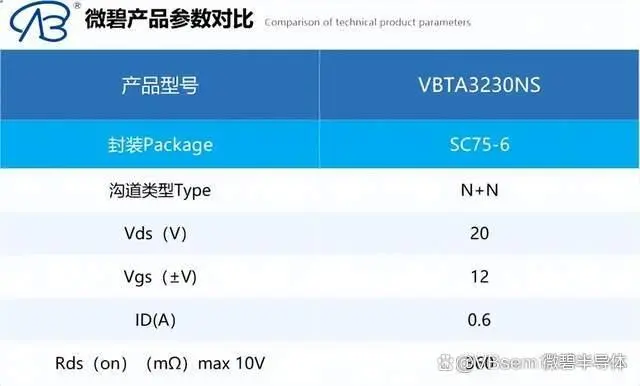
For MOSFET selection, the VBsemi VBTA3230NS dual-channel N+N MOSFET can be used, with Vds=20V, Id=0.6A, and a gate-source threshold voltage of 1V.
Furthermore, the MOSFET's main product packages include: SOP-8, TO-220(F), TO-263, TO-247, TO-252, TO-251, SOT-23, SOT-223, SOT-89, QFN, AO3400, IRF540, IRF630, and other series of packages, widely used in various electronic products such as consumer electronics, security equipment, measurement instruments, radio and television education, home appliances, military/aerospace, wearable devices, automotive electronics, network communications, Internet of Things (IoT), new energy, medical electronics, lighting electronics, smart homes, computer motherboards and graphics cards, MID\UMPC, GPS, Bluetooth headsets, PDVD, car DVD players, car audio systems, LCD monitors, mobile power supplies, mobile phone batteries (lithium battery protection boards), LED power supplies, etc.

After prototype testing, the device can work stably for a long time, with low power consumption. The R-wave positioning accuracy is greater than 96% in motion states, and the heart rate error is less than 4%, demonstrating high data accuracy and reliability.
In conclusion, the application of VBsemi MOSFETs in wearable ECG signal monitoring devices solves the problem of MOSFET switch circuitry switching between charging and power supply states. The widespread application of MOSFETs in various electronic products also provides reliable support for the hardware design of such devices. With the increasing awareness of health, the market demand for wearable ECG monitoring devices will continue to grow, and VBsemi will continue to provide high-quality and reliable electronic components for this field.
* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您