In the previous articles, we often talked about PN junctions, and the parasitic diode in MOS transistors is formed because of the PN junction. Today, let's introduce this diode in detail.

Many people may have this question, what exactly is the function of this diode? What kind of diode is it?
This parasitic diode, also called the body diode, let's take the NMOS transistor as an example to explain how it is formed. The NMOS transistor has a P-type semiconductor substrate, with two trenches dug out on top, and then filled with a heavily doped N-type semiconductor, forming the following structure.
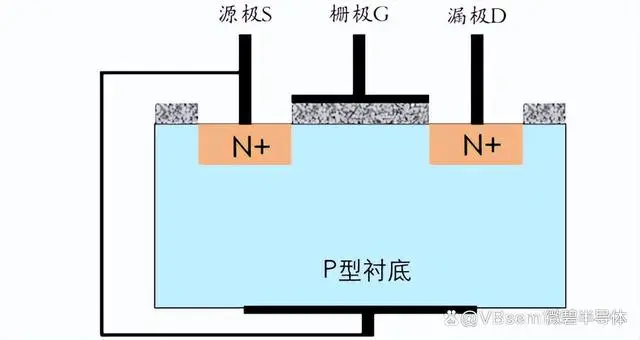
Everyone knows that when P-type and N-type semiconductors are placed together, they will always form a PN junction. So, there should originally be PN junctions between the substrate and the source (S) terminal, and between the substrate and the drain (D) terminal. However, because the source terminal is connected to the substrate, only the PN junction between the drain terminal and the substrate is formed, and this is the body diode formed between the substrate and the drain terminal.
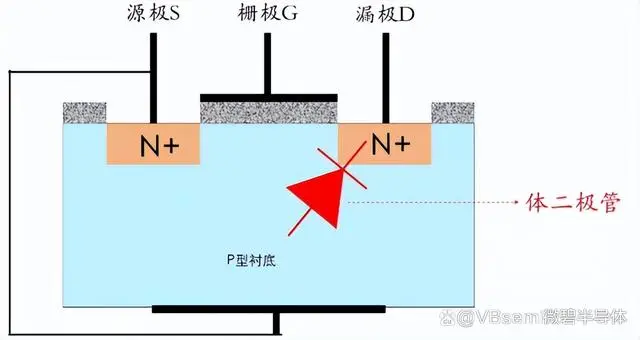
Since the substrate and the source terminal are shorted, it is equivalent to forming a body diode between the source and drain terminals. Moreover, this diode is formed due to the manufacturing process and cannot be avoided.
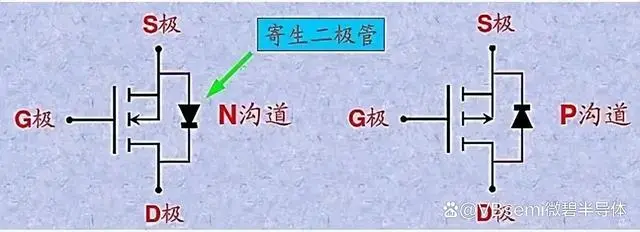
It is worth noting that not all situations require the substrate's B terminal to be connected to the source terminal. For example, in integrated circuits, the B terminal is connected to the lowest or highest voltage, not necessarily the source terminal.
If the B terminal is left floating, then there is no diode between the drain and source terminals, in which case, the drain and source terminals are symmetrical and can be swapped.
So what is the use of this diode? Let's talk about its benefits next. When there is a large instantaneous reverse current in the circuit, it can be led out through this diode, protecting the D and S terminals of the MOS transistor. Without this diode, it is possible to burn out the MOS transistor.
When the source and drain are connected, and VDD is too large, this diode will break down in reverse before causing damage to the MOS transistor, directing the large current directly to ground, thereby avoiding burning out the MOS transistor.
In addition, in some circuits, such as switch mode power supply circuits, this diode can be used to release the energy in the inductor, or in motor controllers, through the diode, to form a rectifier diode.
However, everything has its drawbacks. Let me talk about one small disadvantage of it, which I believe no one will object to.
However, it also has a drawback, which is that it will produce leakage current between the source and drain. This needs to be noted when using MOS transistors.
Alright, that's all about the body diode of the MOS transistor. You can use this diode cleverly when using MOS transistors.
However, everything has its drawbacks. Let me talk about one small disadvantage of it, which I believe no one will object to.
However, it also has a drawback, which is that it will produce leakage current between the source and drain. This needs to be noted when using MOS transistors.
Alright, that's all about the body diode of the MOS transistor. You can use this diode cleverly when using MOS transistors.
* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您