With the number of transistors in a single chip reaching billions or even hundreds of billions, semiconductor companies invest significant manpower, resources, and finances in their creation. Each of these transistors or components can be patented by semiconductor companies. For these companies, holding such a vast array of patents can yield abundant harvests.
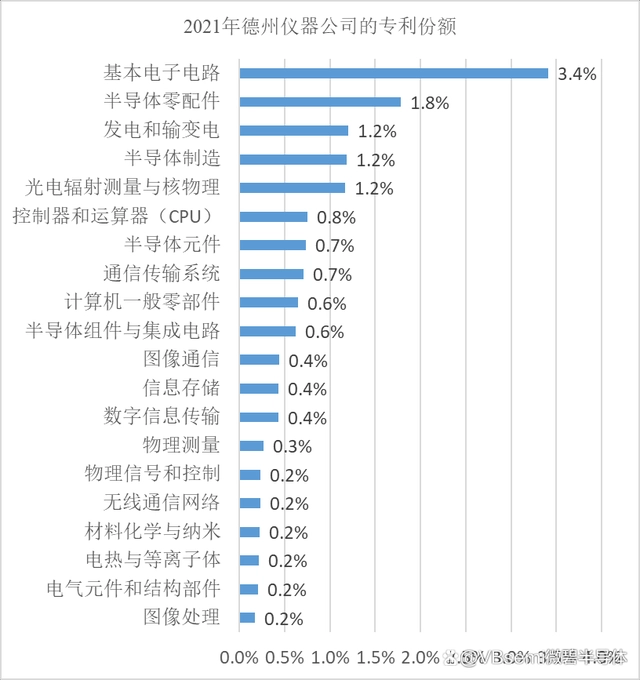
Taking Texas Instruments as an example, its accumulated large number of patents continue to generate substantial income.
Development of patents in the semiconductor industry model.
As we know, the current semiconductor industry model mainly consists of equipment manufacturers, wafer fabs, and foundries. This industry model divides the tasks of the semiconductor industry into finer segments, enabling companies to develop more targeted approaches.
However, in the early stages before EDA tools emerged, chip design was a daunting task, making equipment manufacturers the main players in the industry at that time, and relevant patents naturally revolved around various aspects of equipment manufacturing.
Until the rise of EDA tools, which facilitated the standardization of chip design and gradually separated chip design from manufacturing, wafer fabs and foundries were born.
Companies like Qualcomm and Huawei, which do not have wafer fabs, mainly focus on designing their own products and have applied for a large number of patents in their respective fields.
According to Securities Times, Huawei's patent applications exceeded 10,000 in 2020 and reached 12,000 in 2021. In the past two years, Huawei has continued to research advanced chip technology, such as 3D chip stacking patents and EUV lithography patents, although it faces challenges in export licenses. However, patents are like "strongholds" for Huawei, guarding them allows for the possibility of continued progress.
As for Qualcomm, the patent war between Apple and Qualcomm over baseband chips for mobile phones is still fresh in memory. Although the two eventually settled, Apple signed a six-year patent licensing agreement with Qualcomm as a result, requiring Apple to continue paying hefty patent fees to Qualcomm.
TSMC, as a leader in the wafer foundry field, had over 75,000 global patent applications and over 52,000 granted patents as of May 2022. Among the top 20 semiconductor manufacturers worldwide, TSMC ranks first in patent intensity and second in patent quantity, only behind Samsung.
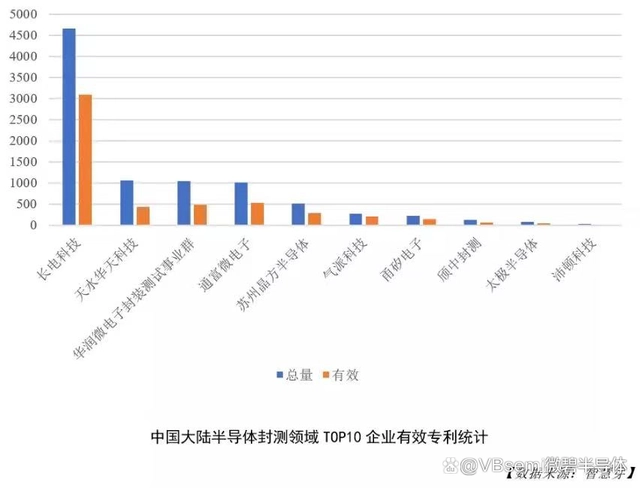
In China, mature outsourcing packaging and testing models have also accumulated a large number of patents. According to data from Wisdom Yaya, Changxin Technology ranks first in the number of effective patents in China's packaging and testing field, with over 3,000 patents. It is also the designated enterprise for packaging and testing of VBsemi products.
Semiconductor manufacturing software, EDA tools, and other related software are becoming increasingly important in the development of chips, and the number of patent applications related to them is increasing year by year.
In summary, equipment manufacturers, wafer fabs, foundries, and software companies are all applying for patents in their respective fields. With more cross-border companies joining the self-developed chip array, new technologies will emerge from the integration of these patents, which will be more conducive to the development of the industry.
A vast array of patents brings abundant harvests to semiconductor companies.
As an important carrier of intellectual property rights, patents represent a significant source of income for companies.
As a global leader in the semiconductor industry, Intel also holds a pivotal position in patents. According to insights.greyb, Intel has over 210,000 patents worldwide. According to Intel's official website, Intel currently holds approximately 70,000 valid patent assets globally.
Top global semiconductor companies such as IBM, Samsung, Qualcomm, Infineon, TSMC, Micron, Apple, and AMD all use Intel's patents.
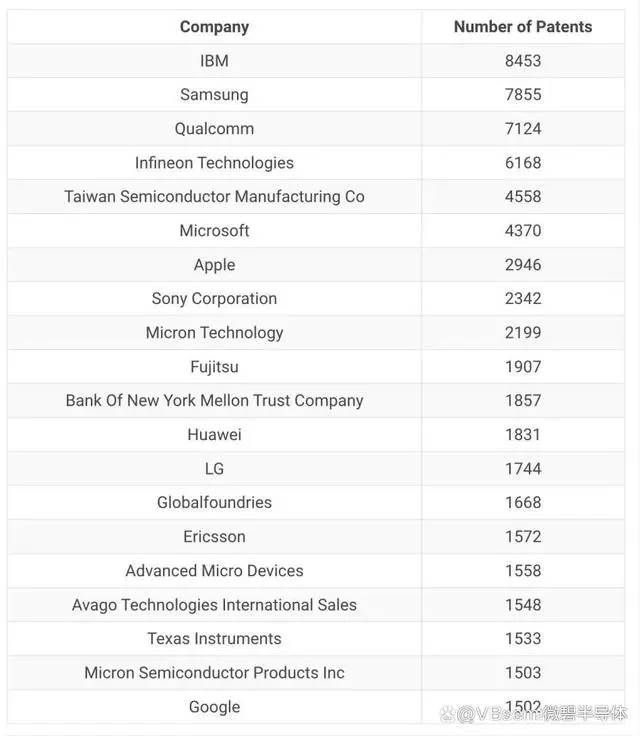
Companies using Intel's patent portfolio In addition to licensing patents, patent transfer is also a way for companies to generate revenue.
In March 2021, Huawei officially announced the collection of 5G patent license fees. As one of the earliest developers of 5G, Huawei can be said to be one of the latest to collect fees.
In the automotive field, approximately 8 million vehicles per year currently deliver to consumers with Huawei 4G/5G patent licenses. Since the beginning of this year, Huawei has reached agreements with approximately 15 automakers, including Mercedes-Benz, Audi, Porsche, and BMW, all of which are seeking to add more communication technologies to their vehicles.
Patent wars are commonplace in any industry, and the collection of patent fees is only the smallest benefit. The deeper significance lies in building a high technological barrier for the company itself, limiting the expansion of competitors. In today's globalized development of enterprises, patents undoubtedly symbolize the discourse power of enterprises in the industry, and even the initiative of countries.
* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您