In a typical example, a MOSFET has a maximum current of 100A and a battery voltage of 96V. When it just enters the Miller plateau after turning on, the MOSFET's power dissipation is P=VI. Since the current reaches its maximum, all the power is dissipated in the MOSFET: P=96100=9600W.
At this point, its power dissipation is at its maximum, and then quickly decreases until it is fully conducting, at which point the power becomes 1001000.003=30W. Assuming the MOSFET's internal resistance is 3 milliohms, the power dissipation during this switching process is quite astonishing.
We know that slowing down the charging can reduce oscillation but will prolong the switch.
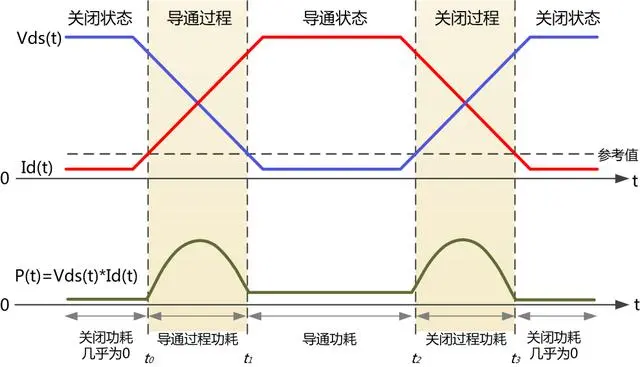
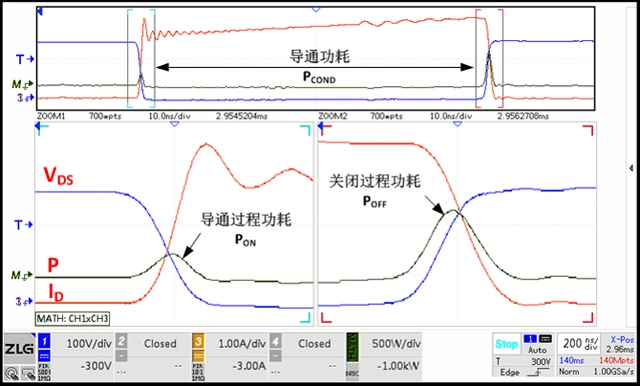
If the turn-on time is slow, it means that the transition from 9600W to 30W of heat dissipation will be slow, leading to a significant increase in the MOSFET's junction temperature and burning of the MOSFET. A long rise time will cause the MOSFET to operate in a linear state rather than a switching state.
We can choose to reduce the current limit of the MOSFET, for example, limit it to 50A, or reduce the battery voltage to 48V. This way, the losses will be halved, avoiding burning the MOSFET.
This is also the reason for the burning of the high-voltage control tube. However, the switching loss of the low-voltage control is different, and its conduction loss is mainly determined by the MOSFET's internal resistance.
This internal resistance decreases as the Vgs voltage increases, so do not assume that as long as the Vgs threshold voltage is exceeded, the MOSFET can be smoothly turned on. Especially in high-power applications, a high Vgs is very necessary, so the heat dissipation of the MOSFET is very important.
So, is faster charging better?
Of course not, too fast charging will lead to severe Miller oscillation.
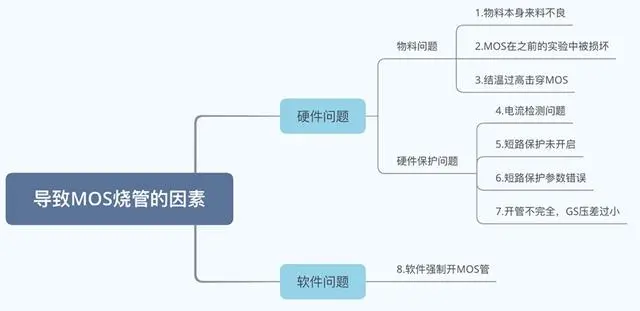
In addition, the heating of the tube at small currents is mainly caused by the following factors: too high frequency, poor heat dissipation design, selection, and circuit design.
Too high frequency: Excessive pursuit of volume, resulting in increased frequency, MOSFET loss increased, increasing heat dissipation.
Heat dissipation design: When the current is too high and the heat dissipation design is not good, the heat dissipation may be serious when ID is less than the maximum current.
Selection has differences: The judgment of power is inconsistent, and the internal resistance of the MOSFET is not fully considered, resulting in an increase in switch impedance.
Circuit design: Causes the MOSFET to operate in a linear state rather than a switching state.
There are also differences between NMOS and PMOS here.
When NMOS is used as a switch, the voltage at the gate needs to be several volts higher than the power supply to fully turn on, but for PMOS, it is the opposite.
Because it is not fully open and the voltage drop is too large, resulting in power consumption, the equivalent DC impedance is relatively large, the voltage drop increases, so U*I also increases, and the loss means heating.
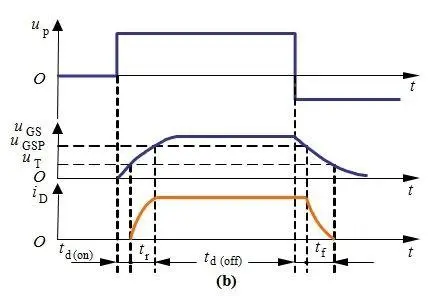
MOSFET conduction process
General solutions:
MOSFET selection: Choose an appropriate internal resistance, not the smaller the better, the larger the cgs and cgd capacitance;
Good heat dissipation design, add enough auxiliary heat sinks;
Here is another question (found online): A MOSFET generally has two current ratings, continuous drain current and pulse current. But in practical applications, can the peak current not exceed the continuous current?
In fact, the pulse current of the MOSFET is instantaneous and cannot be sustained, such as the instantaneous surge current during switching. Generally, the pulse of the MOSFET is very large and if it is continuous output and the output time is relatively long, attention to heat dissipation is also necessary.
Note that if an external heat sink cannot be used, you can try to use a larger package, which will have better heat dissipation performance.
* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您