Theoretically, the upper P-lower N configuration should have advantages. So why is the upper N-lower P configuration commonly used in push-pull circuits?
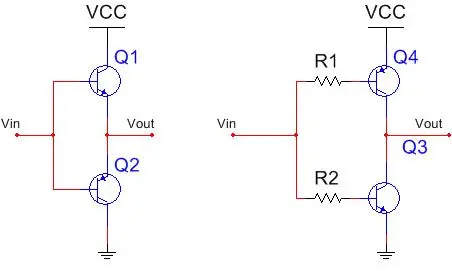
The left diagram represents the upper P-lower N configuration, while the right one represents the upper N-lower P configuration.
In the upper N-lower P configuration, as shown on the right, the output signal has the same phase as the input signal. When the input is high, the output will also be high.
However, based on the characteristics of the N-type transistor, the output voltage amplitude of the N-type transistor is equal to Vb (approximately 0.7V). Therefore, its output amplitude will be limited by the output signal, which strictly requires the amplitude of the input signal. Otherwise, it may lead to insufficient high-level signals in the subsequent stages.
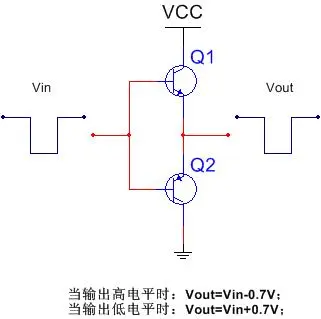
Moreover, when the high-level of the input signal is lower than the power supply voltage, it means that the CE junction of the upper N transistor will bear a higher voltage, posing a risk of heating and damage.
However, the reason why it is commonly used in practical applications is also because the current passing through the transistors in push-pull circuits used for signal control is not very large, so the upper transistor is not easily damaged.
But if the push-pull circuit is applied to drive loads, it may not be the case.
If the current flowing through the transistor is relatively large while the input signal amplitude is low, the upper transistor will generate serious heating.
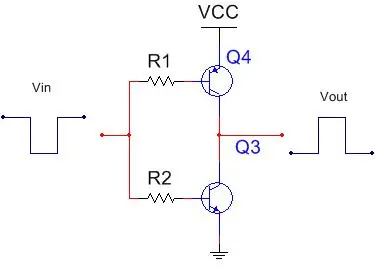
On the other hand, in the upper P-lower N configuration, the output is opposite to the input. When the input is high, the output is low.
Comparing it with the upper N-lower P configuration, we can see that a resistor is connected in series with the base of the transistor in the upper P-lower N configuration. The reason for these two resistors is to isolate the upper P transistor from the lower N transistor. When the P transistor conducts, the signal will flow through the N transistor, which may easily cause the problem of both transistors being conducting simultaneously.

However, adding two resistors poses cost issues, and despite adding resistors, it is still necessary to ensure that the signal amplitude is high enough to avoid the problem of both transistors conducting.

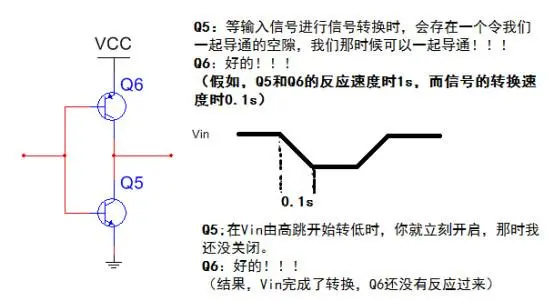
Additionally, there is a possibility of conduction when the signal jumps, so it is necessary to ensure that the transistors complete the signal conversion before making the switch response to avoid conduction.
* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您