A bootstrap circuit is very useful in high-voltage gate driver circuits.
When VS drops to the IC supply voltage VDD or is pulled down to ground, (low-side switch conducts, high-side switch turns off),
the power supply VDD charges the bootstrap capacitor CBOOT through the bootstrap resistor RBOOT and the bootstrap diode DBOOT.
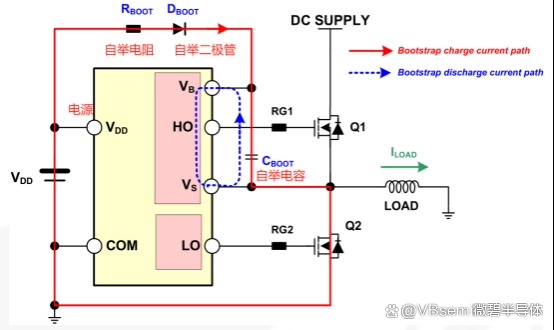
When the high-side switch pulls VS up to a higher voltage, the bootstrap capacitor discharges through VBS, at which point the VBS power supply floats, the bootstrap diode is reverse biased, and the track voltage (low-side switch turns off, high-side switch conducts) and the IC supply voltage VDD are isolated.
The above describes the operation principle of the bootstrap circuit in high-voltage gate driver circuits.
When the input level does not allow direct gate drive circuits for high-side NMOS or IGBT, we can consider bootstrap gate driver technology.
It is often used as gate drive and associated biasing circuits, both of which reference the source of the main switch device.
Bootstrap circuits have the advantages of simplicity and low cost.
However, there are also some drawbacks. The duty cycle and conduction time are limited by the bootstrap capacitor. Additionally, when the switch device is turned off, the negative voltage at the source may cause the load current to suddenly flow through the freewheeling diode, causing trouble for the output of the gate driver circuit.
Furthermore, if the capacitor is too small, excessive ripple occurs when the upper switch is turned on, reducing the lifespan of the capacitor, increasing switch losses, and decreasing switch reliability.
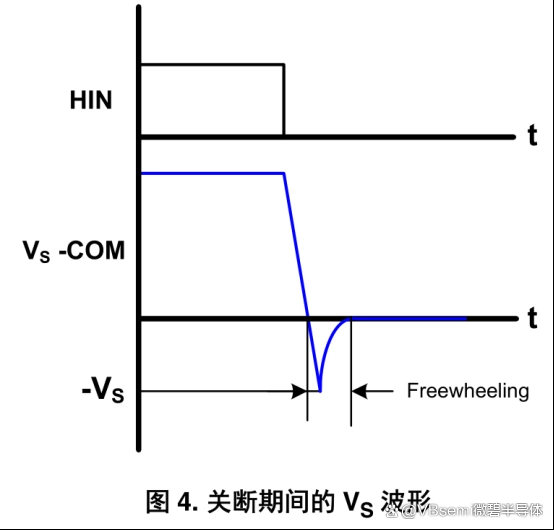
If the capacitance value is too large, the charging time of the bootstrap capacitor is reduced, and the conduction time of the low-side may be insufficient to bring the capacitor to the bootstrap voltage.
In such cases, specific duty cycle compensation or independent power supply may be required in the PWM algorithm.
* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您