Previously, VBsemi published an article titled "Why are Enhancement-Mode NMOS often chosen as switches in power supplies?" which mentioned that in practical applications, we often use enhancement-mode MOSFETs.
But what about the often overlooked depletion-mode ones? Do they serve no other purpose?
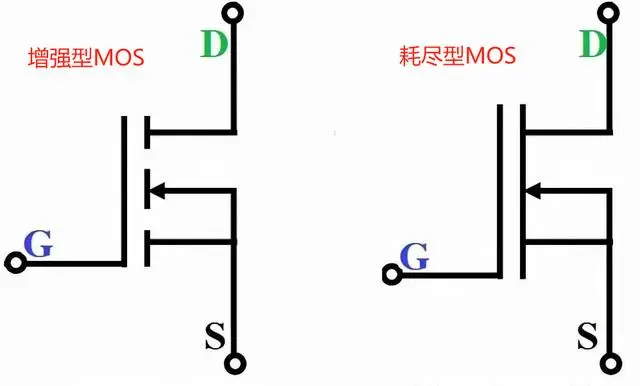
First, let's understand the differences of depletion-mode.
Power MOSFETs are divided into depletion-mode (DM) and enhancement-mode (EM), mainly differing in the conductive channel, and their control methods are different.
The G terminal of a depletion-mode MOSFET has a conductive channel present when no voltage is applied, while an enhancement-mode MOSFET is the opposite, the conductive channel appears only after it is turned on, and its Vgs must be greater than the gate threshold voltage.
The Vgs (gate-source voltage) of a depletion-mode MOSFET can control conduction with positive, zero, or negative voltage. To prevent conduction between the drain and source, a certain negative voltage needs to be applied at the gate, and depletion-mode MOSFETs are often understood as "normally closed switches".
Application Differences
Unlike enhancement-mode MOSFETs, depletion-mode MOSFETs are not used in high-frequency applications.
Apart from linear MOSFETs, enhancement-mode devices cannot operate in linear mode. However, depletion-mode devices have an extended FBSOA (Forward Bias Safe Operating Area), thus they can operate in linear mode.
Depletion-mode MOSFET products are generally applicable in traditional startup circuits, surge protection for linear voltage regulators, constant current sources, high-voltage ramp signal generators, solid-state relays, etc.
Let's briefly explain with traditional startup circuits and linear voltage regulators:
Traditional Resistor-Startup Circuit
Traditional startup circuits often use power resistors to directly supply power to PWM control ICs. However, after the power is started, the resistor continues to consume power, resulting in significant losses. As mentioned above, depletion-mode MOSFETs are normally closed devices, so for zero standby power requirements, depletion-mode MOSFETs become the preferred choice.
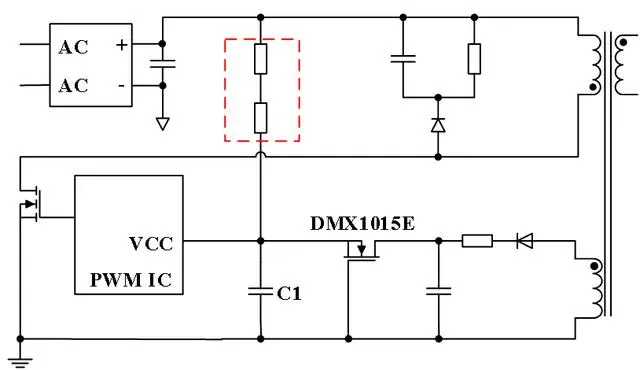
When the gate-source voltage Vgs = 0V, the device channel naturally opens. After the circuit starts, power is supplied to the PWM control IC through the depletion-mode MOSFET, and the current then charges capacitor C1 through the depletion-mode MOSFET, gradually increasing the voltage on C1 until the PWM IC starts working.
Later, power is supplied to the PWM control IC through additional windings. At this point, the gate of the depletion-mode MOSFET is pulled down to a low level via the ASU port, making the gate-source voltage Vgs of the depletion-mode MOSFET greater than its turn-off voltage Vgs (off), thus the depletion-mode MOSFET turns off, and thereafter, no current flows through the circuit, eliminating power losses.
Surge Protection for Linear Voltage Regulators
Linear voltage regulators are small analog circuits that provide power to CMOS ICs or any other loads requiring low current, with the input voltage Vin directly from the bus voltage. This may result in large voltage variations, including voltage spikes caused by application environments.
Depletion-mode MOSFETs are used for surge protection in linear voltage regulator circuits, employing a source follower configuration, where the voltage on the source follows the voltage on the gate. The conduction of the depletion-mode MOSFET depends only on the gate voltage and is independent of the drain-source voltage.
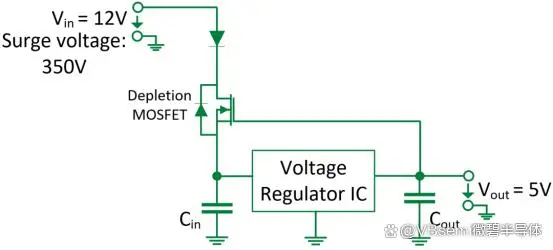
This configuration is generally aimed at reducing voltage transients until the device reaches its rated voltage tolerance Vds. This is based on the wide DC operating voltage range Vin of the depletion-mode MOSFET and its ability to achieve minimal power consumption with low static currents.
Such protection functions can be used in communication applications to reduce transient effects caused by surges and can also be used in automotive or aviation electronic applications to reduce transients caused by inductive loads.
However, depletion types are divided into N-channel and P-channel. In the manufacture of NMOS, a large amount of Na+ or K+ positive ions are doped at the SiO2 insulation layer, while negative ions are doped in the manufacture of PMOS. When Vgs = 0, the electric field generated by the positive ions can induce enough electrons in the P-type substrate, forming an N-type conductive channel.
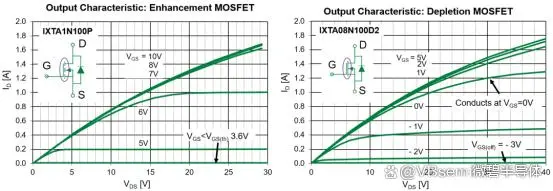
When Vgs > 0, a larger ID (drain current) will be generated; when Vgs < 0, it weakens the electric field formed by the ions, causing the N-channel to narrow and reducing the ID current.
In practical applications using depletion-mode MOSFETs, it may trigger the MOSFET erroneously when the device is powered on, leading to the failure of the entire system, making it difficult to control. This is also why depletion-mode MOSFETs have very few applications.

* 如果您需要申请我司样品,请填写表格提交,我们会24小时内回复您